Anhedonie-Test: Wie Ernährung Ihre Freude zurückgewinnen helfen kann
November 27, 2025 | By Corina Valerio
Haben Sie bemerkt, dass Essen nicht mehr so befriedigend schmeckt wie früher? Wenn Sie unter Anhedonie leiden – der anhaltenden Unfähigkeit, Freude zu empfinden –, können sogar Ihre Lieblingsgerichte fade und uninteressant wirken. Wenn Sie mit dieser emotionalen Taubheit kämpfen, sind Sie nicht allein. Aktuelle Forschung zeigt einen starken Zusammenhang zwischen dem, was Sie essen, und der Fähigkeit Ihres Gehirns, Freude zu verarbeiten. Dieser Leitfaden beleuchtet wissenschaftlich fundierte Ernährungsstrategien, die Ihre emotionale Reaktionsfähigkeit unterstützen können, und betont, dass das Verständnis Ihrer Symptome durch einen validierten kostenlosen Anhedonie-Test der entscheidende erste Schritt auf Ihrem Weg zu mehr Wohlbefinden ist.
Die Darm-Gehirn-Verbindung: Erkenntnisse aus Ihrem Anhedonie-Test
Was in Ihrem Darm geschieht, bleibt nicht im Darm – es kommuniziert direkt mit Ihrem Gehirn über die Darm-Hirn-Achse. Diese bidirektionale Autobahn erklärt, warum Verdauungsprobleme oft mit Stimmungsveränderungen einhergehen.
Die Rolle des Mikrobioms bei der Stimmungsregulation
Ihr Darmmikrobiom – Zuhause von Billionen von Bakterien – produziert 90 % des Serotonins Ihres Körpers, des Neurotransmitters, der für Stimmungsstabilität und Freudeempfindung essenziell ist. Studien zeigen, dass probiotikareiche Lebensmittel Folgendes bewirken können:
- die Sensitivität von Dopaminrezeptoren erhöhen
- entzündungsfördernde Moleküle reduzieren
- die Nährstoffaufnahme verbessern
Entzündung: Die verborgene Verbindung zwischen Ernährung und emotionaler Taubheit
Chronische Entzündungen wirken wie Rauschen auf den Belohnungskreis Ihres Gehirns. Stark verarbeitete Lebensmittel lösen die Produktion von Zytokinen aus, die:
- Dopaminbahnen schädigen
- die neuronale Plastizität in den Freudezentren reduzieren
- oxidativen Stress im Gehirngewebe erhöhen
Wenn Entzündungen anhalten, registrieren sogar normalerweise angenehme Aktivitäten keine Belohnung mehr – ein Kennzeichen der Anhedonie. Diese Verbindung unterstreicht, warum Ihr wissenschaftlicher Anhedonie-Test wichtige Muster aufdecken könnte, die einen Gespräch mit einem Ernährungsberater wert sind.
Wichtige Nährstoffdefizite, die mit Anhedonie-Symptomen in Verbindung stehen
Forschung identifiziert spezifische ernährungstechnische Lücken, die Anhedonie-Symptome verschlimmern können. Konsultieren Sie immer Ihren Arzt vor der Einnahme von Nahrungsergänzungsmitteln, da diese Mängel oft mit anderen Erkrankungen überlappen:
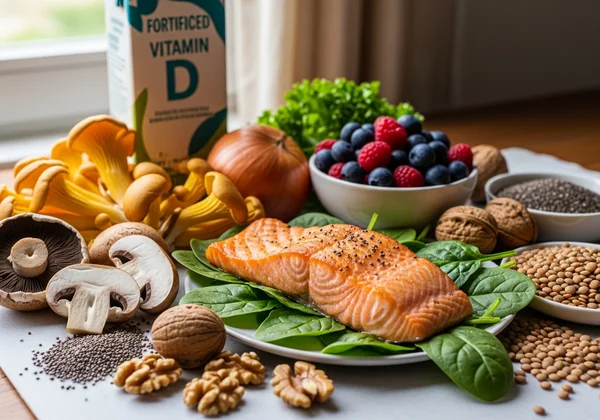

Vitamin D: Die Auswirkungen des Sonnenvitamins auf die Belohnungsverarbeitung
Über 40 % der Erwachsenen mit Stimmungsstörungen weisen einen Vitamin-D-Mangel auf. Dieser Nährstoff:
- Reguliert Tyrosinhydroxylase (das Enzym, das Dopamin herstellt)
- Schützt Dopaminneurone vor oxidativen Schäden
- Verbessert glutamaterge Signale, die an der Vorwegnahme von Freude beteiligt sind
Lebensmittelquellen: Fettreicher Fisch, UV-bestrahlte Pilze, angereicherte Pflanzenmilch
B-Vitamine: Essentiell für die Neurotransmitterproduktion
Mängel an B9 (Folat) und B12 korrelieren stark mit der Schwere der Anhedonie. Diese Nährstoffe:
- Helfen bei der Umwandlung von Tryptophan in Serotonin
- Unterstützen Methylierungsprozesse, die für die Dopaminsynthese entscheidend sind
- Myelinscheiden erhalten, die Neuronen der Belohnungspfade schützen
Lebensmittelquellen: Linsen, Spinat, Nährhefe, Eier
Omega-3-Fettsäuren: Unterstützen die Kommunikation zwischen Gehirnzellen
EPA- und DHA-Omega-3-Fettsäuren machen 30 % der Gehirnzellmembranen aus. Humanstudien belegen, dass sie:
- Das Volumen der grauen Substanz in belohnungsrelevanten Regionen erhöhen
- Neuroinflammation in nur 8 Wochen reduzieren
- Dopaminfreisetzung und Rezeptorsensitivität steigern
Lebensmittelquellen: Walnüsse, Chiasamen, Algenöl, Sardinen
Neugierig, wie Ihre Symptome mit diesen Mängeln übereinstimmen? Kombinieren Sie Ernährungsumstellungen mit Erkenntnissen aus einem validierten Screening-Tool für personalisierte Anleitungen.
Anhedonie-Diät: Lebensmittel, die die emotionale Verarbeitung unterstützen
Probiotikareiche Lebensmittel für die Darmsgesundheit
Wählen Sie mindestens eine tägliche Portion aus:
- Fermentiertes Gemüse: Sauerkraut, Kimchi (ungepasteurisiert wählen)
- Fermentierte Milchprodukte: Kefir, Joghurt (nach „lebenden aktiven Kulturen“ suchen)
- Fermentierte Tees: Kombucha (zuckerarme Varianten)
Diese Lebensmittel liefern nützliche Bakterien, die die emotionale Verarbeitung innerhalb von 4 Wochen verbessern können. Um zu sehen, wie Ihre aktuelle Ernährung Ihre Symptome beeinflusst, nehmen Sie einen schnellen Selbsttest vor.
Antioxidantienreiche Früchte und Gemüse
Priorisieren Sie tief pigmentierte Sorten:
- Beeren: Wildblaubeeren (Anthocyane schützen Dopaminneurone)
- Blattgemüse: Spinat, Mangold (reich an stimmungsunterstützendem Magnesium)
- Kreuzblütler: Brokkolisprossen (Sulforaphan reduziert neuronale Entzündungen)
Proteinquellen für Neurotransmitter-Unterstützung
Streben Sie 20–30 g Protein pro Mahlzeit aus folgenden Quellen an:
- Tryptophanquellen: Pute, Kürbiskerne, Tofu
- Tyrosinquellen: grasgefüttertes Rindfleisch, Mandeln, Hüttenkäse
- Pflanzliche Kombinationen: Brauner Reis + schwarze Bohnen, Hummus + Vollkorn-Pita
Diese Proteine liefern Vorläufermoleküle, die Ihr Gehirn benötigt, um „Wohlfühl“-Neurotransmitter herzustellen.
Ernährungsstrategien zur schrittweisen Umsetzung

Einfache Mahlzeiten-Tauschideen zur Steigerung der Nährstoffaufnahme
- Statt Frühstückscerealien → Haferflocken mit Walnüssen, Chiasamen und Beeren
- Soda ersetzen → Sprudelwasser mit Zitrone und Minze
- Chips austauschen → Geröstete Kichererbsen mit Kurkuma
- Statt Süßigkeiten → Zartbitterschokolade (70 %+ Kakao)
Zu erwägende Nahrungsergänzungsmittel (mit fachlicher Beratung)
Besprechen Sie diese Optionen mit Ihrem Arzt:
- Vitamin D3: 1000–4000 IE/Tag abhängig von Blutwerten
- Omega-3: 1000–2000 mg EPA/DHA-Kombination
- Methylfolat: Aktive B9-Form (besonders bei MTHFR-Mutation)
- Probiotika: Nach Stämmen wie Bifidobacterium longum 1714™ suchen
Lebensmittel, die Sie einschränken oder meiden sollten
- Ultraverarbeitete Snacks: Stören die Darmvielfalt
- Zugesetzte Zucker: Lösen Dopamin-Spitzen und -Abstürze aus
- Transfette: Fördern Neuroinflammation
- Übermäßiger Alkohol: Verarmt B-Vitamine und Magnesium
Wichtig: Ernährungsumstellungen wirken am besten, wenn sie auf Ihre spezifischen Symptome abgestimmt sind. **Nehmen Sie sich 5 Minuten Zeit für einen vertraulichen Selbsttest, um Ihre Bedürfnisse besser zu verstehen, bevor Sie Ihre Ernährung umkrempeln.
Ihren Weg zur emotionalen Wiederentdeckung nähren
Während kein einzelnes Lebensmittel Anhedonie „heilt“, schafft strategische Ernährung die biochemische Grundlage für eine verbesserte emotionale Verarbeitung. Indem Sie sich auf darmfördernde Probiotika, entzündungshemmende Antioxidantien und neurotransmitterbildende Proteine konzentrieren, stärken Sie die angeborene Fähigkeit Ihres Gehirns, Freude zu empfinden.
Denken Sie daran:
- Auf Hinzufügen konzentrieren: Priorisieren Sie, was Sie Ihrer Ernährung hinzufügen können, nicht nur Einschränkungen.
- Geduldig sein: Darm-Gehirn-Verbesserungen können 4–8 Wochen dauern, bis sie spürbar werden.
- Fortschritt überwachen: Führen Sie ein Ernährungs-Stimmungs-Tagebuch, um Veränderungen zu beobachten.
- Mit Profis zusammenarbeiten: Ernährungsstrategien ergänzen – ersetzen aber nicht – therapeutische Unterstützung.
Wundern Sie sich, wie Ihre Ernährung Ihre Fähigkeit beeinflusst, Freude zu empfinden? Ihre Reise zur emotionalen Wiederentdeckung beginnt mit dem Verständnis Ihrer einzigartigen Muster. Machen Sie unseren validierten Screening-Test und starten Sie durch.

Häufig gestellte Fragen zur Ernährung und Anhedonie
Kann Ernährung wirklich einen Unterschied bei der Behandlung von Anhedonie machen? Ja – aber als Teil eines umfassenden Ansatzes. Forschung zeigt, dass Ernährungsverbesserungen die Wirksamkeit von Medikamenten oder Therapien steigern, Entzündungen reduzieren, die mit emotionaler Taubheit verbunden sind, und Neuroplastizität in den Belohnungspfaden des Gehirns unterstützen können. Nutzen Sie unser klinisch validiertes Tool, um vor Veränderungen eine Baseline zu etablieren.
Wie lange dauert es, bis Ernährungsumstellungen die Stimmung beeinflussen? Die meisten Studien zeigen spürbare Verbesserungen der emotionalen Reaktionsfähigkeit innerhalb von 8–12 Wochen, obwohl Veränderungen im Darmmikrobiom bereits nach Tagen beginnen können. Kombinieren Sie ernährungstechnische Strategien mit kognitiven Techniken für verstärkte Effekte. Ein guter erster Schritt ist, Ihre Baseline zu verstehen, um den Fortschritt genau zu tracken.
Gibt es spezifische Nahrungsergänzungsmittel, die bei Anhedonie helfen? Einige Forschungen unterstützen Omega-3, Vitamin D und spezifische Probiotika, aber die Wirksamkeit hängt von individuellen Mängeln ab. Sehen Sie sie als Wegweiser zu gezielten Interventionen. Entdecken Sie Ihre Anhedonie-Risikofaktoren durch unsere personalisierten Berichte.
Wie hängt die Darmsgesundheit mit der Fähigkeit zur Freudeempfindung zusammen? Ihr Darmmikrobiom produziert Neurotransmitter (wie Serotonin und Dopamin), reguliert Entzündungen, die die Belohnungszentren des Gehirns beeinflussen, und beeinflusst die Aufnahme von Nährstoffen, die für die Stimmungsregulation notwendig sind. Der tiefe Einfluss des Darms unterstreicht die Notwendigkeit einer kollaborativen Gesundheitsführung.
Sollte ich meine aktuelle Behandlung durch Ernährungsumstellungen ersetzen? Unterbrechen Sie niemals verschriebene Behandlungen ohne ärztlichen Rat. Verwenden Sie stattdessen einen Drei-Schritte-Ansatz:
- Bewerten Sie Ihre Symptome mit unserem vertraulichen Screening-Tool.
- Besprechen Sie die Ergebnisse mit Ihrem Behandlungsteam.
- Integrieren Sie Ernährung als evidenzbasiertes Ergänzungsmittel zu Ihrem Plan.
Denken Sie daran: Anhedonie ist vielschichtig. Ihr effektivster Ansatz kombiniert professionelle Unterstützung mit auf Ihre einzigartige Biologie abgestimmten Lebensstilstrategien.